Well, let me tell you about this thing called a MOSFET switch. Now, I ain’t no scientist, but I can tell you that it’s somethin’ mighty useful, especially when you’re tryin’ to turn things on and off electronically. A MOSFET, or Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor, is just a fancy name for a little gadget that helps control the flow of electricity in a circuit. Think of it like a gatekeeper—only lets the electricity through when it’s supposed to. You can use it for all sorts of things, like turning lights on or off or controlling motors in machines.
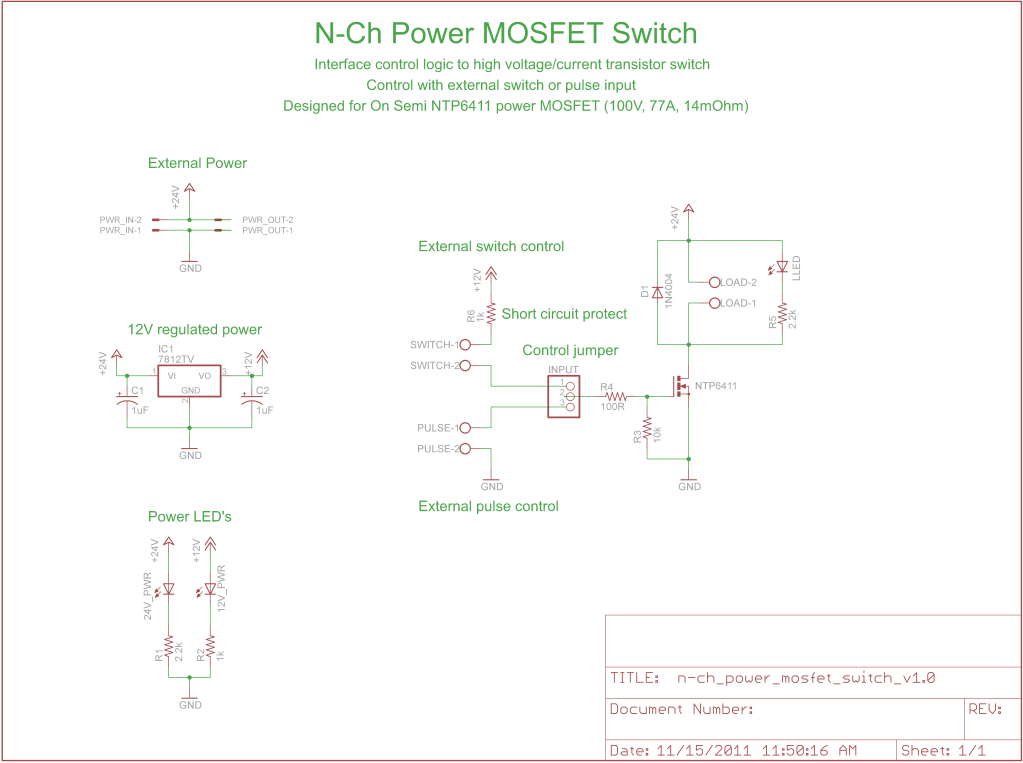
Now, don’t go gettin’ too confused with all these big words. It’s just a switch that works without you havin’ to flip no physical switch. You know, like them fancy newfangled dimmer switches folks are puttin’ in their kitchens these days. The MOSFET switch can be used in all sorts of devices, from your everyday household gadgets to big industrial machines. It helps save on power and is real efficient. No need for a bunch of wires and mess. Just use that MOSFET and you’re good to go.
Now, MOSFETs come in two types: N-channel and P-channel. I ain’t no expert, but let me tell you what I know. The N-channel MOSFET is the one most folks use for their switches. It works like this: when you apply a voltage to the gate, it lets the current flow between two other parts of the device, just like opening a valve. Without the voltage, the current won’t flow. Simple enough, right? It’s kind of like how you open the gate to let the cows out to pasture. If the gate’s closed, no cows are comin’ out.
For the P-channel type, it’s the opposite. You apply voltage, and it stops the current. So, it’s used in situations where you want to turn something off when you apply a voltage. It’s like turnin’ off the water in the garden by closing the valve. Some circuits use both types of MOSFETs to control different parts, depending on whether they want to turn things on or off. Pretty clever, huh?
Now, let me tell you about the different parts of a MOSFET. There’s the drain, the source, and the gate. The source is where the current comes in, the drain is where it goes out, and the gate is what you use to control it. When you apply voltage to the gate, it either lets the current flow or stops it, depending on whether you’re usin’ an N-channel or P-channel. And this is all done without any moving parts, which makes it real reliable. Ain’t no need for switches that might wear out after a while.
One of the most important things to understand is the MOSFET’s behavior in different regions. The MOSFET has three main regions: the cutoff, the linear, and the saturation regions. In the cutoff region, the MOSFET acts like a completely closed switch—no current flows through it. In the linear region, the MOSFET is like a partially open switch, where the current can flow but it’s controlled more precisely. And in the saturation region, the MOSFET is fully on, letting all the current flow through just like a wide-open gate.
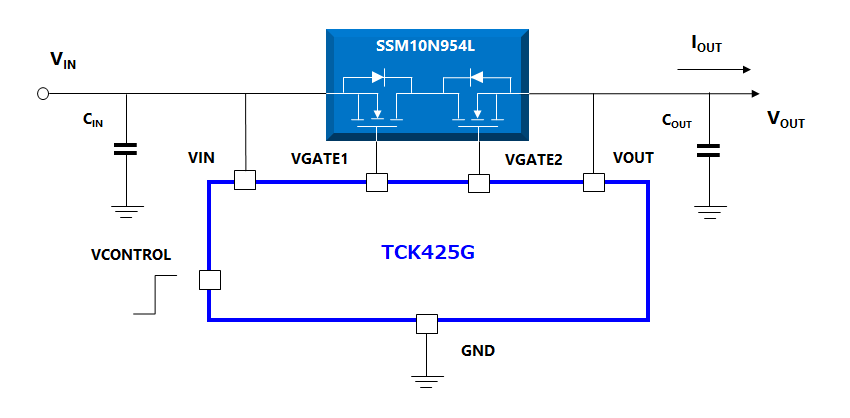
When you’re usin’ a MOSFET switch, it’s important to make sure it’s in the right region for what you want to do. If you want the switch to be off, you want it in the cutoff region. If you want it to be on, you want it in the saturation region. And if you want it to act more like a dimmer, where it’s controlling the current but not completely on or off, then you want the linear region.
So, how do you use one of these in a circuit? Well, first you gotta figure out what kind of load you’re tryin’ to control. A load could be anything that uses electricity—like a light bulb, a fan, or a motor. Once you know what you want to control, you can build your circuit around the MOSFET. It’s usually pretty simple, just a few parts and some wire. You hook up the source to the power supply, the drain to the load, and the gate to a control voltage that’ll turn the switch on or off.
There’s plenty of examples out there for different circuits you can build with MOSFETs. You can use them in things like power supplies, where you need to switch on a big load, or in logic circuits, where you need to turn things on and off in a very controlled manner. It’s real handy, and once you get the hang of it, you’ll see just how much you can do with ‘em.
Now, if you’re worried about the MOSFET gettin’ too hot or burnin’ out, you’ll want to make sure you use one with the right ratings. Some MOSFETs can handle more power and voltage than others, so you need to pick the right one for your application. If you pick the wrong one, well, let’s just say it’s not gonna last long. But if you choose right, you’ll have yourself a reliable switch that’ll work for a long time.
In conclusion, MOSFET switches are a real handy tool for controlling electrical circuits. Whether you’re usin’ an N-channel or P-channel MOSFET, or just need a simple way to turn things on and off, these little devices do the job. They’re efficient, reliable, and can be used in all sorts of applications. So if you’re messin’ around with electronics, don’t be afraid to give a MOSFET switch a try—you might be surprised at how easy and useful it is.
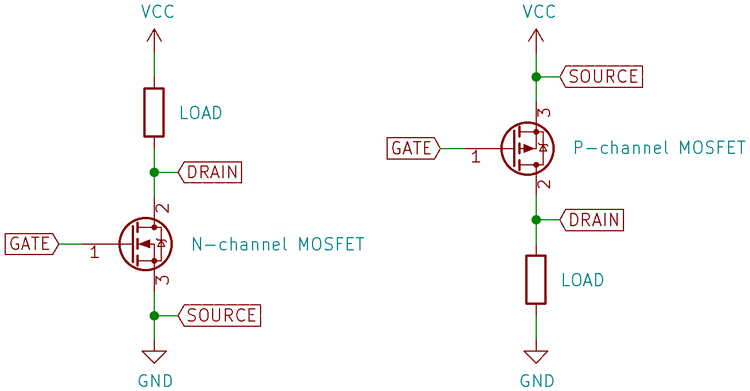
Tags:[MOSFET Switch, Electronic Switch, Power MOSFET, N-channel MOSFET, P-channel MOSFET, MOSFET Circuit, Voltage Control, Load Control, Electronics for Beginners]

